WHAT IS THERMOGRAPHY ?
Nowadays there is an increasing interest in innovative techniques used to inspect the internal part of materials to check if some flaws are present inside it, to have a quantitative measure of its mechanical properties. The main goal of these innovative techniques is to test the material without destroying it and for this reason these techniques are called non-destructive inspection techniques (NDT).
Thermography is an NDT technique that allows detecting flaws inside a material by mean of observing it with a thermal camera. It is largely diffusing among industries and it's becoming a must in the quality checks and inspection phase.
There are applications also in the medical field, for illness (like diabetes and vascular disorder) and tumour detection.
In this article I will describe the working principle of thermography, providing some examples of real applications.
How thermography works
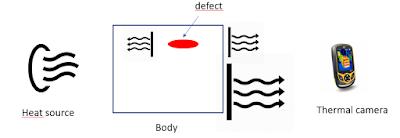
Thermography is based on the observation of a body using a thermal camera, exploiting the fact that a material emits infrared radiation depending on its surface and internal composition. Indeed, a change in chemical composition or the presence of flaws influences how heat is emitted.
Knowing the fact that heat emission and transmission change with the internal conformation of material, we can exploit this behaviour to identify flaws and defects.
Thermography techniques
There are two main categories of thermography techniques:
Thermal Imaging technique (TIT): it is based on the passive observation of the body, without heating it before with the usage of a heating source. This is used, for example, to find out short circuits, since where a short-circuit happens heat is emitted.
Transient Thermography: It is based on the observation of a body that is previously heated with a heating source like a halogen lamp. This technique is divided again into other two categories, depending on how the body is heated and observed.
- Transmission Thermography: the body is heated from one side and observed with a thermal camera on the other side. The presence of a defect reflects thermal waves and slows down the heat transmission. For this reason, defects will appear cooler.
- Reflection Thermography: the body is heated and observed from the same side. In this case, since the presence reflects thermal waves, these regions will appear hotter.
Another technique is vibrothermography and it consists of exciting the component under inspection which vibrations and observe. Vibrations induce heating and for this reason, regions where defects are present will appear hotter. however, this is not a very diffused technique.
Thermography applications
The most diffused usage of thermography is oriented to flaw detection, in particular in composite materials. Composite materials are prone to have many defects, like delaminations, interlaminar or intralaminar cracks. In the picture below, a debonding between stiffeners and composite panel is shown.
There are applications also in concrete structures, where thermography can be used to detect concrete spalling. In this case, a strong Sun exposition is needed to obtain a good resolution.
Thermography is also used to monitor industrial processes and to measure stresses.
Another diffused application concerns the identification of defects in buildings insulation. With thermography, it is possible to find regions where insulation is not well realized, identifying leakages, especially in correspondence of doors and windows. Also, moisture penetration through walls or roofs and can be identified, since the presence of moisture changes the thermal conductivity.
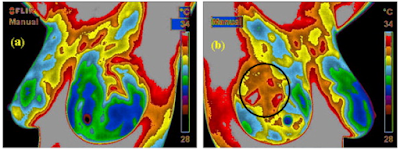
Finally, thermography allows identifying the illness state of a patient, since usually temperature increase occurs. An example is Mammography, where breast tumour is identified using thermography: in fact, tumoral cells require an increased blood supply that makes temperatures increasing.
In literature, many other applications can be found.
Conclusions
In this brief article, I presented the Thermography technique. Thermography is really useful in defects detection and is becoming a diffused techniques in industries, both for quality checks and inspection. The biggest advantage is that Thermography is an NDT, allowing the inspection of material without destroying it. This allows decreasing times and costs.
ScienceFull.






Comments
Post a Comment